TCP-socket关闭后端口仍然占用
在使用TCP做一些数据传输的测试时发现,Server端程序关闭再启动时常常会出现该地址或端口已被占用的错误(关闭时socket已经释放),如下是python脚本执行时错误打印:
1 | Traceback (most recent call last): |
关闭脚本使用的是”Ctrl+C”按键组合,代码中会监听SIGINT信号,在信号处理函数中关闭Server socket
1 | def handler(signal_num,frame): |
为什么已经释放的socket再次绑定时会出现地址被占用的错误?
使用netstat命令查看占用的端口,发现存在一个处于TIME_WAIT的连接
1 | [root@localhost awokezhou]# netstat -tn | grep "9091" |
TCP连接状态
查看RFC-793文档,阅读了其中和TCP状态转换相关的内容
Connect States
RFC-793中定义了一个TCP Connect在其生命周期的所有状态,原文如下
- LISTEN represents waiting for a connection request from any remote TCP and port
- SYN-SENT represents waiting for a matching connection request after having sent a connection request
- SYN-RECEIVED represents waiting for a confirming connection request acknowledgment after having both received and sent a connection request
- ESTABLISHED represents an open connection, data received can be delivered to the user. The normal state for the data transfer phase of the connection
- FIN-WAIT-1 represents waiting for a connection termination request from the remote TCP, or an acknowledgment of the connection termination request previously sent
- FIN-WAIT-2 represents waiting for a connection termination request from the remote TCP
- CLOSE-WAIT represents waiting for a connection termination request from the local user
- CLOSING represents waiting for a connection termination request acknowledgment from the remote TCP
- LAST-ACK represents waiting for an acknowledgment of the connection termination request previously sent to the remote TCP (which includes an acknowledgment of its connection termination request)
- TIME-WAIT represents waiting for enough time to pass to be sure the remote TCP received the acknowledgment of its connection termination request
- CLOSED represents no connection state at all
一个TCP连接共有11种状态:LISTEN、SYN-SEND、SYN-RECEIVED、ESTABLISHED、FIN-WAIT-1、FIN-WAIT-2、CLOSE-WAIT、CLOSING、LAST-ACK、TIME-WAIT和CLOSED
重点关注和连接关闭有关的几个状态
- FIN-WAIT-1 等待远端的连接终止请求,或者等待自己发送的连接终止请求被远端确认
- FIN-WAIT-2 等待远端的连接终止请求
- CLOSE-WAIT 等待本地用户的连接终止请求
- CLOSING 等待自己发送的连接终止请求被远端确认
- LAST-ACK 等待自己发送的连接终止请求被远端确认
- TIME-WAIT 表示等待足够的时间以确保远端收到自己的终止请求确认
- CLOSED 表示连接已经被完全关闭
只从字面意思理解,这几个状态有很多相似的地方,并不能理解到每个状态位于什么阶段
状态转移
RFC-793文档中有一个TCP连接的状态转换示意图
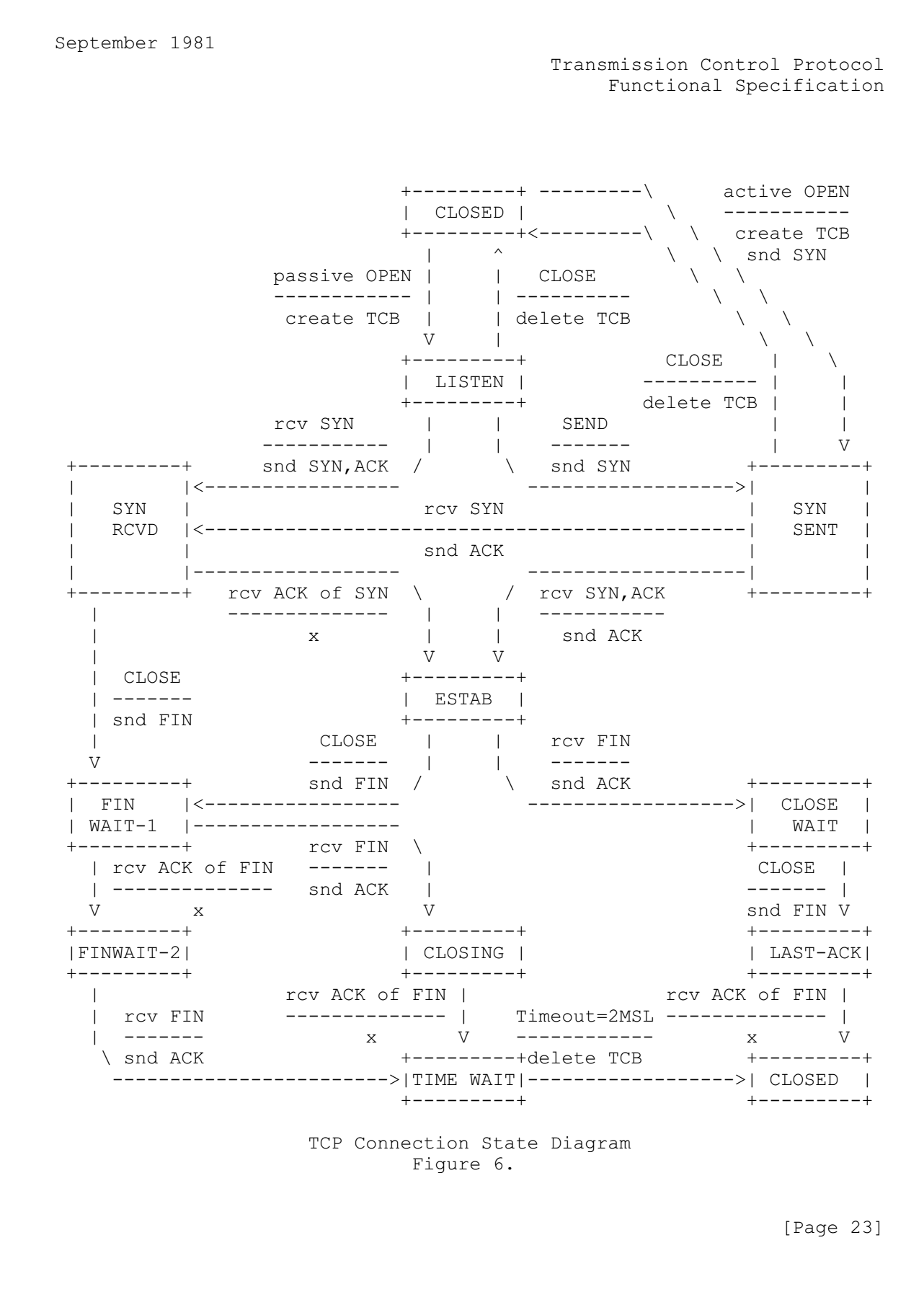
由该图可以看出以下区别
- FIN-WAIT-1 有两种情况会触发该状态:
- Server端在接收到Client端的连接请求后就主动关闭连接,向Client发送FIN后立即进入
FIN-WAIT-1状态 - 建立连接后(双方都进入
ESTABLISHED),任何一方主动关闭连接,向对端发送FIN后立即进入FIN-WAIT-1状态
- Server端在接收到Client端的连接请求后就主动关闭连接,向Client发送FIN后立即进入
- FIN-WAIT-2 只有处于
FIN-WAIT-1的一方收到对方的FIN ACK后,立即进入该状态 - CLOSE-WAIT 建立连接后,收到远端FIN后,回复FIN ACK,立即进入该状态
- CLOSING 只有处于
FIN-WAIT-1的一方收到对方FIN后,进入该状态 - LAST-ACK 只有处于
CLOSE-WAIT的一方主动关闭连接,向对方发送FIN后,进入该状态 - TIME-WAIT 只有处于
FIN-WAIT-12的一方收到对方FIN后,进入该状态
按照该图的状态转移流程,其实主要的转移路线有以下两条:
1 | FIN-WAIT-1 --> FIN-WAIT-2 --> TIME-WAIT --> CLOSED |
这两条路线的区别在于谁先发起连接终止请求,也就是谁先关闭socket
MSL
先关闭连接的一方最终会进入TIME-WAIT状态,由TIME-WAIT状态切换到CLOSED状态,但是中间需要等待一个超时时间2MSL。正是由于这个2MSL超时时间的存在,导致Server再次bind时发生错误
提出以下3个问题
- 什么是MSL,为什么需要MSL?
- 先关闭的一方,接收到对端的FIN,发送FIN ACK后直接释放连接资源不行吗,为什么需要等待2个MSL时间?
- 后关闭的一方,为什么不需要MSL?
什么是MSL
MSL英文全称是”Maximum Segment Lifetime”,即TCP片的最大存活时间
RFC-793原文中对于MSL的解释如下
1 | Knowing When to Keep Quiet |
大意为:为了确保TCP不会创建一个序列号与网络中已经存在的分片序列号重复的分片,在分配新的序列号之前必须在MSL时间内保持静默。标准规定的MSL时间为2分钟,是一个基于工程经验的选择
TIME-WAIT后为什么需要等待2个MSL?
为了保证处于FIN-WAIT-2状态(记为A)时发送的最后一个ACK能够到达对端(记为B)。最后一个ACK可能在网络中丢失,使得B处于LAST-ACK状态无法进入CLOSED状态。B会超时重传这个FIN,A发送ACK丢失+B重传FIN到达A,这个时间刚好是2倍的MSL
后关闭的一方,为什么不需要2MSL?
2MSL本质上是在等待最后一个ACK,后关闭的一方是FIN的发送方,等待ACK,有重传机制作保障,其状态是可控的,因此不需要其他等待超时
测试
环境介绍
Server端 centos7虚拟机,IP地址172.16.79.132, python2.7,创建socket绑定localhost、9091端口
Client端 windows10,IP地址172.16.79.182,python2.7,创建socket向Server发起连接
linux 使用如下命令查看连接状态
1
netstat -tn | grep '9091'
windows使用如下命令查看连接状态
1
netstat -tn | findstr '9091'
创建连接
Server创建socket代码
1 | import socket |
Client创建socket并向
1 | import socket |
查看Server连接状态
1 | [root@localhost awokezhou]# netstat -tn | grep "9091" |
查看Client连接状态
1 | λ netstat -tn | findstr '9091' |
双方都进入了ESTABLISHED状态,表明连接建立成功
Server先关闭socket
Server关闭连接
1 | c.close() |
查看Server连接状态
1 | [root@localhost awokezhou]# netstat -tn | grep "9091" |
查看Client连接状态
1 | λ netstat -tn | findstr '9091' |
Client关闭连接
1 | c.close() |
查看Server连接状态
1 | [root@localhost awokezhou]# netstat -tn | grep "9091" |
查看Client连接状态
1 | λ netstat -tn | findstr '9091' |
Server最终进入了TIME-WAIT状态,Client连接已经释放。如果此时关闭并重启Server,在调用bind时就会报错
Client先关闭socket
Client关闭连接
1 | s.close() |
查看Server连接状态
1 | [root@localhost awokezhou]# netstat -tn | grep "9091" |
查看Client连接状态
1 | λ netstat -tn | findstr '9091' |
Server关闭连接
1 | c.close() |
查看Server连接状态
1 | [root@localhost awokezhou]# netstat -tn | grep "9091" |
查看Client连接状态
1 | λ netstat -tn | findstr '9091' |
Client再次发起连接
1 | s = socke.socket() |
查看Client连接状态
1 | λ netstat -tn | findstr '9091' |
上一个连接还处于TIME-WAIT状态,但是又创建了一个新的连接。如果重启Client并不会报错,因为Client不用bind端口和地址
总结
socket关闭后端口仍然占用的错误原因是Server端先关闭了连接,再次重启时旧连接并未释放,而是处于TIME-WAIT状态导致的。解决该问题有如下几种方法
- Server端创建socket时设置端口重用
SO_REUSEADDR - 等待2MSL超时之后再创建socket
- Server端不要先关闭连接,让Client先关闭连接
Reference
RFC-793 PDF
服务器大量的fin_wait1 状态长时间存在原因分析
网络的FIN_WAIT_2状态解释和分析
TCP 协议(TIME_WAIT 状态
TCP TIME-WAIT
TCP在FIN_WAIT1状态到底能持续多久以及TCP假连接问题
防止linux出现大量 FIN_WAIT1,提高性能
深入理解TCP(2)TCP的断开一定是四次挥手吗?FIN_WAIT_2和CLOSE_WAIT,TIME_WAIT以及LAST_ACK的细节
TCP/IP中MSL详解
Time-wait状态(2MSL)一些理解